Mechanical waves, such as sound waves, are a fascinating aspect of physics. They require a medium—be it solid, liquid, or gas—to propagate. But what happens when there is no medium, like in a vacuum? Can mechanical waves travel through such an environment, or are they limited by the absence of matter?
What is a Mechanical Wave?
A mechanical wave is a disturbance that moves through a material medium due to the interaction between particles within that medium. These waves rely on the transfer of energy through the medium’s particles. Common examples of mechanical waves include sound waves, water waves, and seismic waves.
Types of Mechanical Waves
Mechanical waves can be categorized into two main types:
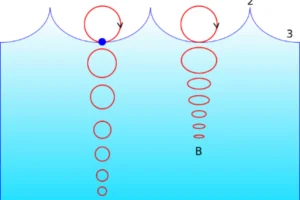
- Transverse Waves: In these waves, the displacement of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of the wave. A classic example is waves on a string.
- Longitudinal Waves: Here, the displacement of the medium is parallel to the direction of the wave. Sound waves in the air are a prime example of longitudinal waves.
The Need for a Medium
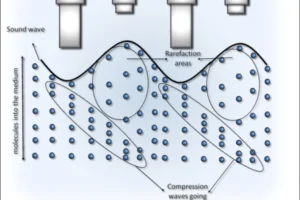
For mechanical waves to propagate, they require a medium because the wave is essentially a transfer of energy between particles. In the case of sound waves, air molecules vibrate and pass the energy along, creating the sound we hear. Similarly, seismic waves travel through the Earth’s crust, relying on the material’s properties to move energy from one place to another.
What is a Vacuum?
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter, meaning it contains no particles that can vibrate or interact with each other. In such an environment, there are no atoms or molecules to carry the energy of a mechanical wave, making it impossible for these waves to propagate.
Can Mechanical Waves Travel Through a Vacuum?
The simple answer is no. Mechanical waves cannot travel through a vacuum because they depend on the interaction between particles in a medium to transmit energy. Without any particles to interact with, the wave has no way to move or propagate.
Comparison with Electromagnetic Waves
Unlike mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to propagate. They can travel through the vacuum of space because they consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that can move independently of matter. This is why light from the sun can reach Earth, even though the space between them is mostly a vacuum.
Practical Implications
Understanding that mechanical waves cannot travel through a vacuum has significant implications in various fields. For instance, space is silent because there is no medium to carry sound waves. Similarly, seismic waves cannot travel through the vacuum of space, limiting their reach to within the Earth’s layers.
Mechanical waves are bound by the necessity of a medium to propagate. In a vacuum, where no medium exists, these waves cannot travel. This distinction is crucial in understanding the nature of different types of waves and their applications in science and technology.








